Ansible is a popular configuration automation tool that helps to automate infrastructure processes without exposing credentials. The Ansible integration helps IT administrators and process analysts to create Ansible playbooks to automate the administration tasks and commands. Integrating Ansible with OpsRamp helps to do agentless automation tasks for process workflows.
The Ansible integration is available only at the client level.
Target users: Client administrators and process analysts
Why use Ansible integration?
The Ansible integration enables the following:
- Automating workflows using SSH without installing agents on all the remote systems.
- Performing auto-remediation actions.
- Scheduling tasks.
- Executing an ad hoc workflow.
Integrating Ansible with OpsRamp
The Ansible integration involves installing Ansible and creating playbooks. One Ansible integration can have multiple playbooks. Every playbook represents an automation script in the YAML format. The playbook is assigned to a process automation workflow to execute the related automation tasks.
Prerequisites
- Install Ansible on one of the servers in a specific environment (Ansible Control Node).
- Verify if the target managed nodes and hosts are accessible through SSH with the Ansible Control Node.
- Copy the full path of each Ansible script with the file name to create a playbook.
- Allow OpsRamp URL in the Ansible server to download all the latest Agent packages. To download, go to the OpsRamp Console and navigate to Setup > Downloads > Agent.
Sudopermissions are required for the device user.- Verify if the Ansible Control Node is visible and active at OpsRamp Console by navigating to Setup > Infrastructure.
Install Ansible integration
Install the Ansible integration directly from the OpsRamp console. Before starting the installation, verify if the host name and Ansible server are visible on the Infrastructure > Resources page.
- Navigate to Setup > Account.
- Select the Integrations and Apps tile.
- The Installed Integrations page, where all the installed applications are displayed.
- If there are no installed applications, it will navigate to the Available Integrations and Apps page.
- Click +Add on the Installed Integrations page. The Available Integrations and Apps page displays all the available applications.
- Search for the application using the search option available. Alternatively, use the All Categories option to search.
- Click +Add on the Ansible tile.
- Enter the following details:
- Name: Enter the name for the integration.
For example, Ansible playbook automation. - Controller Host Name: Select a name from the available options. The drop-down menu displays Ansible Control nodes configured with an OpsRamp agent.
- Name: Enter the name for the integration.
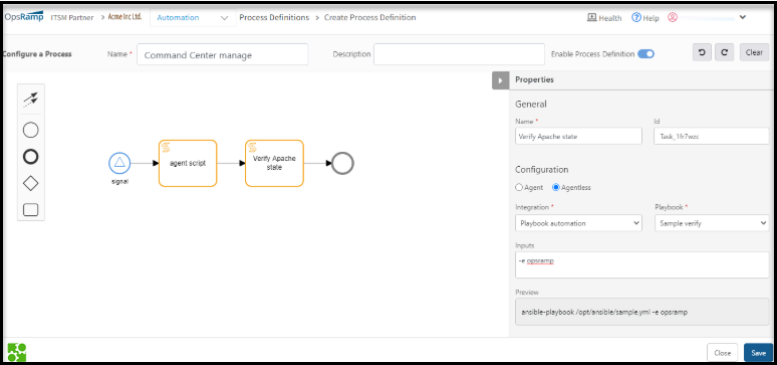
Add playbooks
Add one or more playbooks. One playbook can execute only one automation script.
Example: Find ipconfig details.
Prerequisite: Keep handy the name and complete path of the script required for creating a playbook.
- From the Playbook section, click +Add.
- In the Add Playbook dialog box, provide a name for the playbook.
Example: Check Server. - Enter the complete path of the script.
- (Optional) In the Input field, enter more parameters for the script.
- Click Add Playbook.
The new playbook is added. An integration can have one or more playbooks. To add more playbooks, click Add.
To update an existing playbook, click the menu (three dots) icon and select Edit. - Click Finish.
- The playbook added with the installed integration is ready to use in a process workflow.
Actions on Integration
You can perform actions on the Ansible integration.
- See here for more information.
Using Ansible integration
The installed Ansible integration is used while creating business process workflows. See Getting Started with Process Definition for more information.
Verify if the installed integration is active.