Introduction
Kubernetes events provide critical insights into the state of your cluster resources—such as Pods, Deployments, and Nodes. They help you:
- Monitor application and cluster state
- Detect and respond to failures
- Perform troubleshooting and diagnostics
In Kubernetes 2.0, the OpsRamp Agent can export Kube Events as:
- Logs
- Alerts
- Both
Note
To export events as logs, ensure Log Management is enabled at the client levelPrerequisites
- During installation of the Kubernetes 2.0 Agent, ensure that the Kube Events option is enabled.
- For details, refer to the Agent Installation Guide.
Steps to Configure
Step 1: Check for Existing ConfigMap
Run the following command to verify if the ConfigMap exists:
kubectl get configmap opsramp-k8s-events-user-config -n <agent-installed-namespace> -oyamlSample ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: opsramp-k8s-events-user-config
labels:
app: opsramp-k8s-events
namespace: {{ include "common.names.namespace" . | quote }}
data:
eventsConfig.yaml: |
# There is a universal LOG management setting for all logs.
# Only if LOG management setting is enabled, logs_enabled setting for kube-events will be effective.
logs_enabled: true
alerts_enabled: false
namespaces:
event_types:
include_involved_objects:
Pod:
include_reasons:
- name: Failed
- name: InspectFailed
- name: ErrimageNeverPull
- name: Killing
- name: OutOfDisk
- name: HostPortConflict
- name: Backoff
Node:
include_reasons:
- name: RegisteredNode
- name: RemovingNode
- name: DeletingNode
- name: TerminatingEvictedPod
- name: NodeReady
- name: NodeNotReady
- name: NodeSchedulable
- name: NodeNotSchedulable
- name: CIDRNotAvailable
- name: CIDRAssignmentFailed
- name: Starting
- name: KubeletSetupFailed
- name: FailedMount
- name: NodeSelectorMismatching
- name: InsufficientFreeCPU
- name: InsufficientFreeMemory
- name: OutOfDisk
- name: HostNetworkNotSupported
- name: NilShaper
- name: Rebooted
- name: NodeHasSufficientDisk
- name: NodeOutOfDisk
- name: InvalidDiskCapacity
- name: FreeDiskSpaceFailed
Other:
include_reasons:
- name: FailedBinding
- name: FailedScheduling
- name: SuccessfulCreate
- name: FailedCreate
- name: SuccessfulDelete
- name: FailedDeleteStep 2: Edit the ConfigMap
kubectl edit cm opsramp-k8s-events-user-config -n <agent-installed-namespace>This will open the ConfigMap in your default editor where you can make changes.
Step 3: Update Parameters
Modify fields such as:
logs_enabled/alerts_enabled→ enable/disable logs or alertsnamespaces→ filter by namespaceevent_types→ filter by event type (Normal/Warning)include_involved_objects→ filter by object type and reasons
Step 4: Save & Apply Changes
Save the ConfigMap changes. Updates will automatically reflect in the OpsRamp portal as new events occur.
Configuration Options
Namespace Filtering
Users can specify a list of namespaces they are interested in; by default, all namespace events are exported.
Example:
data:
eventsConfig.yaml: |
# There is a universal LOG management setting for all logs.
# Only if LOG management setting is enabled, logs_enabled setting for kube-events will be effective.
logs_enabled: true
alerts_enabled: false
namespaces: ["default", "agent-namespace", "kube-system"]Event Type/Level Filtering
Users can provide a list of event types they wish to monitor. Currently, Kubernetes supports two types of events: Normal and Warning.
Example:
data:
eventsConfig.yaml: |
# There is a universal LOG management setting for all logs.
# Only if LOG management setting is enabled, logs_enabled setting for kube-events will be effective.
logs_enabled: true
alerts_enabled: false
namespaces: ["default", "agent-namespace", "kube-system"]
event_types: ["Warning"]Object/Kind Filtering
Users can select specific object types for which they want to receive events and specify reasons for those kinds. Additional attributes can also be added for each reason.
If the “severity” attribute is included, it will generate alerts with the appropriate severity level.
Example:
include_involved_objects:
Pod:
include_reasons:
- name: Failed
- name: InspectFailed
- name: ErrimageNeverPull
- name: Killing
- name: OutOfDisk
- name: HostPortConflict
- name: Backoff
attributes:
- key: severity
value: WarningEvent Reason Filtering
Users may select an “Other” category and provide any reasons of interest. The reasons specified in include_reasons will be exported regardless of the associated object.
Example:
Other:
include_reasons:
- name: FailedBinding
- name: FailedScheduling
- name: SuccessfulCreate
- name: FailedCreate
- name: SuccessfulDelete
- name: FailedDeleteWhen users edit the ConfigMap, the OpsRamp portal will reflect these updates in real-time as corresponding events occur within the cluster. This format organizes the information into clear sections, making it easier to read and understand while maintaining all essential details.
View Events in OpsRamp Portal
- Navigate to Infrastructure > Logs in the OpsRamp portal.
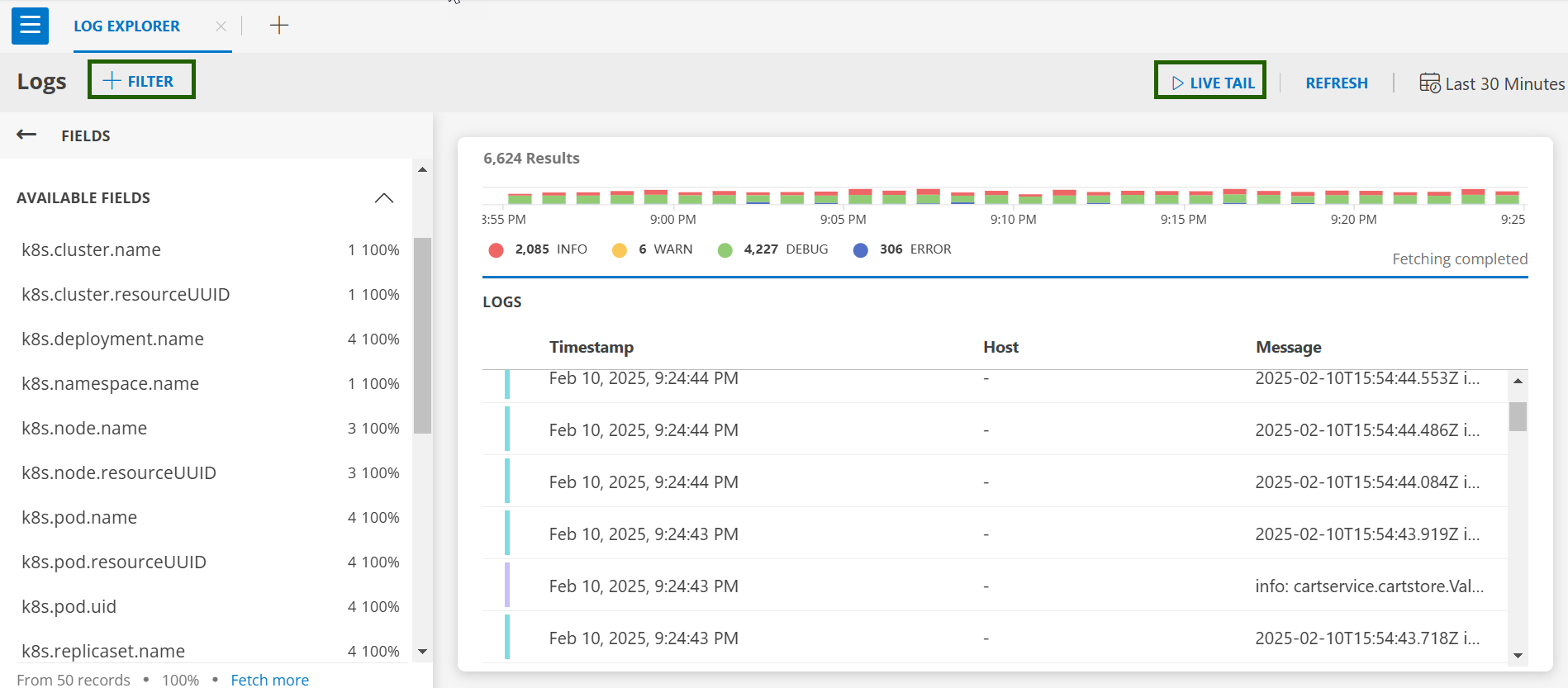
- The Default Logs Screen is appeared.
- Click on +FILTER and search for
type = eventsto see the list of events.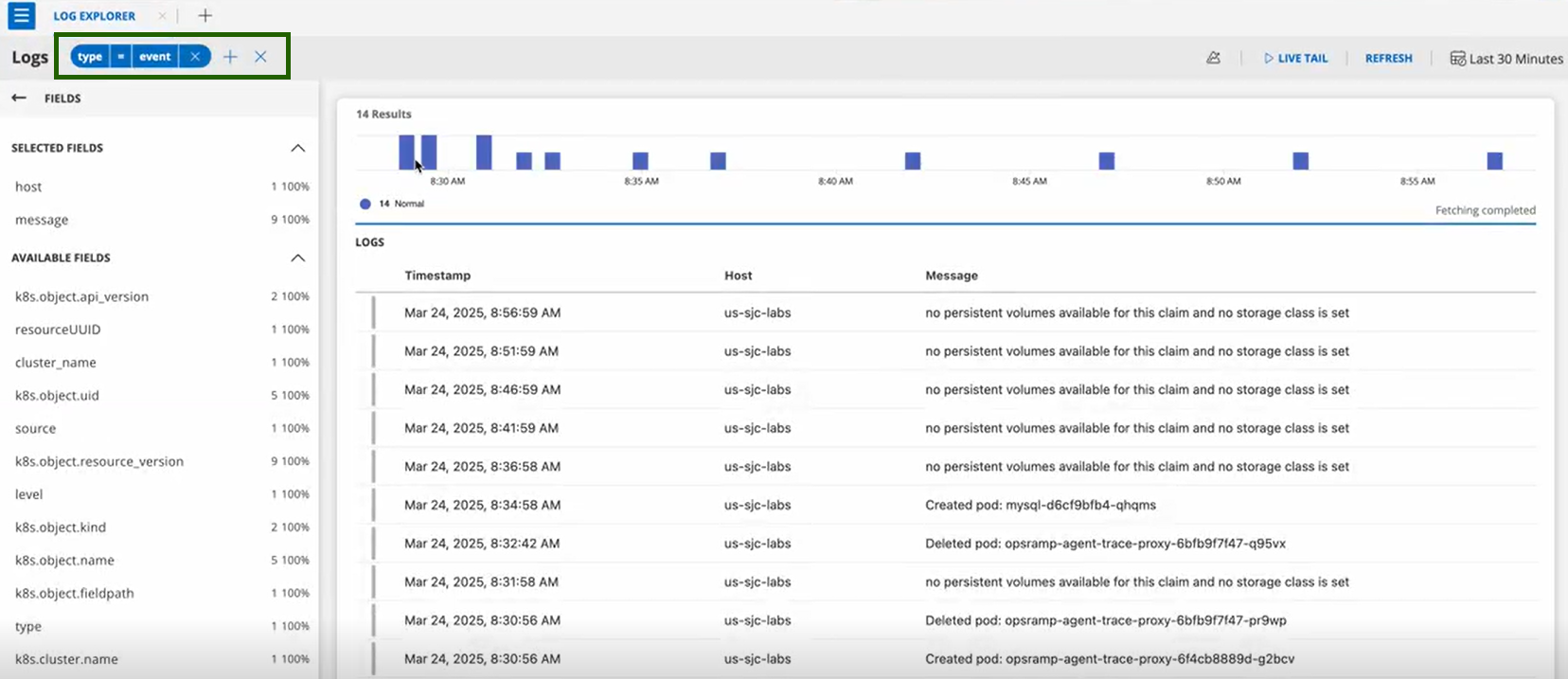
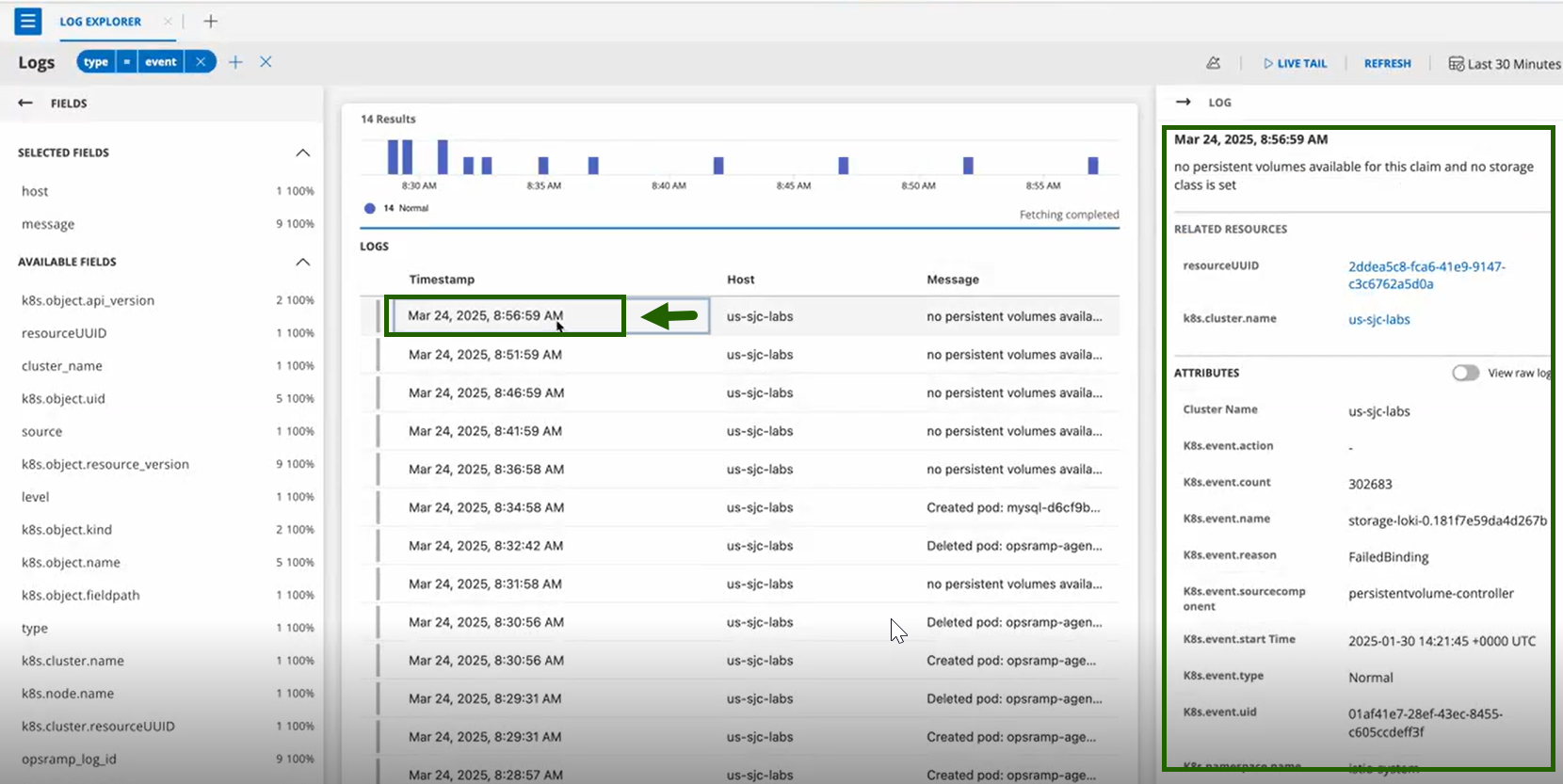
- Click on any event entry for detailed information.
Once you edit the K8s ConfigMap and apply it to your cluster, the OpsRamp Agent will pick up the latest configuration changes within a few minutes. This version organizes the content into clear sections and uses straightforward language for better understanding.
Key Points to Note
- In the log listing UI, the Host column will be empty. Instead, a Resource Name column is displayed, showing the name of the Kubernetes resource associated with the event—for example, the Pod name if the event pertains to a Pod.
- Kubernetes events are now automatically linked to the corresponding resource in OpsRamp. If the resource doesn’t exist, the event links to the cluster.
- Field Differences Between Kubernetes 1.0 and 2.0
- Kubernetes 1.0: The Resource field displays either the IntegrationName or KubeMaster.
- Kubernetes 2.0: The Resource field shows the name of the object that triggered the event as much as possible.
Example: For a Pod Killing event, the Resource will show the Pod name if the Pod’s resourceUUID is available. If not, it will fall back to displaying the cluster name.
- The metric name changed from KubeEvents to kubernetes_events.
- The component format changed to objectUuid - eventReason.
- Some additional attributes have been added based on the event type.
- Alerts do not auto-heal; they must be manually suppressed or resolved.
Troubleshooting
If you encounter kube events issues, see the Troubleshooting documentation.